
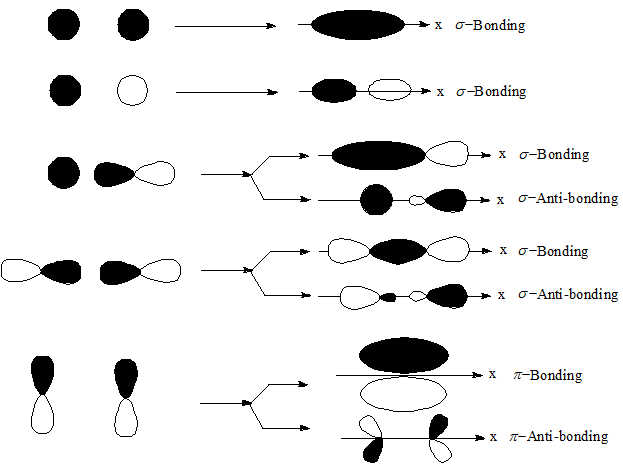
pi bond between two atoms is formed only in addition to a sigma bond. Combining the in-phase orbitals results in a bonding orbital. Read Sign in Contents Chemistry Fundamentals Chapter 7: Advanced Theories of Covalent Bonding 7. The reason is that the overlapping of atomic orbitals can take place to a greater extent during the formation of a sigma bond, whereas overlapping of orbitals occurs to a smaller extent during the formation of a pi bond. (7.3) A bond formed by end-on overlap of atomic orbitals. One contains the axis, and one contains the perpendicular. (21.6) A unit that measures the effect of radiation on the human body Sigma () bond. Combining the out-of-phase orbitals results in an antibonding molecular orbital with two nodes. The valence orbitals in an isolated oxygen atom are a 2 s orbital and three 2 p orbitals. Side-by-side overlap of each two p orbitals results in the formation of two π molecular orbitals. 11 1440 A sigma bond can be formed by overlap of an s atomic orbital with a p atomic orbital. Hybrid orbitals will always overlap head to head to form sigma bonds. The hybrid orbitals about a central atom always are directed at the bonded atoms. For the out-of-phase combination, there are two nodal planes created, one along the internuclear axis and a perpendicular one between the nuclei.įigure 7.7.6. The orbitals that overlap to form the sigma bonds must overlap head to head or end to end. Electrons in this orbital interact with both nuclei and help hold the two atoms together, making it a bonding orbital. Sigma bonds arent necessarily between two s-orbitals. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d ) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3 ) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (,, , ) forms or bonds. functions (orbitals) combine to form hybrid atomic orbitals (sp, sp2, sp3). considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. In molecular orbital theory, we describe the \pi orbital by this same shape, and a \pi bond exists when this orbital contains electrons. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. In valence bond theory, we describe π bonds as containing a nodal plane containing the internuclear axis and perpendicular to the lobes of the p–\pi orbitals, with electron density on either side of the node. This is basically a head-on overlap of orbitals that. The side-by-side overlap of two p orbitals gives rise to a pi (\pi) bonding molecular orbital and a \pi* antibonding molecular orbital, as shown in Figure 7.7.6. Sigma bonds are generated formed when hybrid orbitals overlap with each other along the bonding axis. Combining wave functions of two p atomic orbitals along the internuclear axis creates two molecular orbitals, σp and σ∗p. Just as with s-orbital overlap, the asterisk indicates the orbital with a node between the nuclei, which is a higher-energy, antibonding orbital.įigure 7.7.5. The atomic orbitals overlap along the inter-nuclear axis and involve end-to-end or head-on overlap. There is an \ce^* (antibonding) (read as “sigma-p-x” and “sigma-p-x star,” respectively). A sigma bond can also be formed by the overlap of two p orbitals. Explanation: Sigma Bond: This type of covalent bond is formed by the axial overlapping of half-filled atomic orbitals.
The graphical formulae of two of these isomers are given.This electronic structure adheres to all the rules governing Lewis theory.

(b) There are five structural isomers of the molecular formula C5H10 which are Alkenes. (ii) State the trend in the boiling points from Ethene to Pent-1-ene.
#Bonds formed from atomic s orbitals are always sigma bonds. series#
(i) Give one structural feature of the compounds that makes them members of the homologous series of Alkenes. (a) Four members of the homologous series of Alkenes are Ethene, Propene, But-1-ene and Pent-1-ene.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
